Researchers turned superglue into an recyclable, cheap, oil-free plastic alternative
Researchers have developed a method for producing strong plastic materials by tweaking the chemical structure of superglue.

The Research Brief is a short take about interesting academic work.
The big idea
Our team used superglue as a starting material to develop a low-cost, recyclable and easily produced transparent plastic called polyethyl cyanoacrylate that has properties similar to those of plastics used for single-use products like cutlery, cups and packaging. Unlike most traditional plastics, this new plastic can be easily converted back to its starting materials, even when combined with unwashed municipal plastic waste.
To make a plastic from superglue, we first had to address the very issue that makes superglue so “super” – it sticks to just about everything. When superglue is used to stick something together, it is actually reacting with moisture in the air or on the surface of whatever is being glued together. This reaction forms molecular chains of repeating superglue units called polymers. The polymers made when gluing something together are short and don’t bind to each other well, which makes the glue brittle and easy to break.
While short polymers are good for glue, long polymers have more binding locations and result in stronger materials. Our team realized that if we could create longer versions of the same type of polymers made from superglue, we might be able to produce a strong plastic.

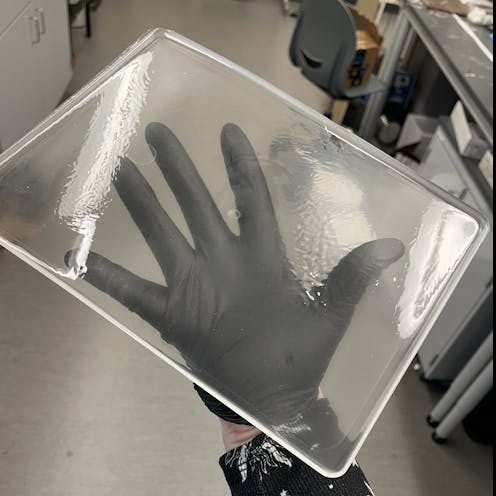
The way we make these plastics is relatively simple when compared with how other types of plastics are made – we simply mixed acetone and a little bit of an eco-friendly catalyst into store-bought superglue. Once this mixture dries, it produces a solid, glassy plastic made up of long polymer chains.
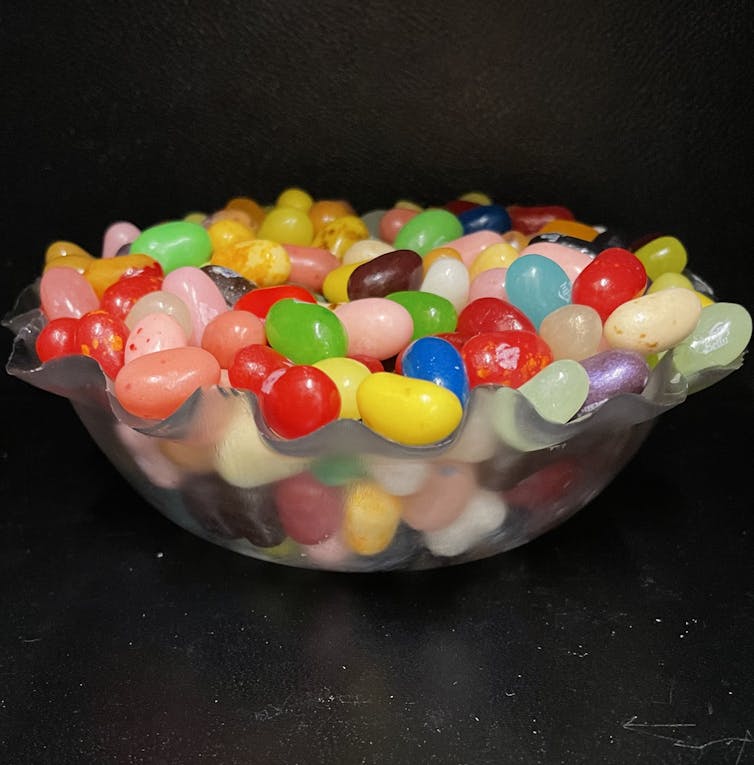
In our lab, we can easily produce up to 10 pounds of this material in a matter of days and turn it into usable products. By pouring the mixture into molds before it dries, we can make plastic objects in many shapes, like bowls and cutlery. We also discovered that heating up the plastic after it dries not only allowed us to shape the material into other products, but also strengthened the plastic.
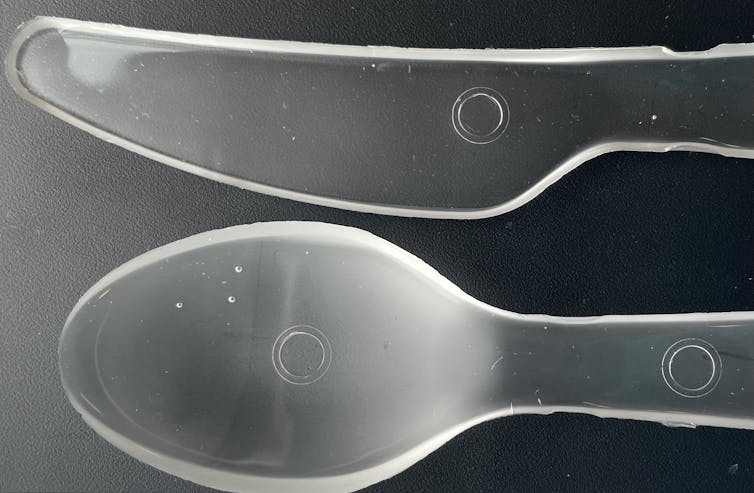
Why it matters
When manufacturers need to produce a stiff plastic object – like cutlery, disposable razors, CD cases or plastic models – they often turn to polystyrene. Polystyrene is one of the most widely produced and least recycled types of plastic.
Because our superglue plastic has properties similar to polystyrene – it is light, durable, cheap and easy to mass-produce – it could replace polystyrene in many products. But there are two distinct benefits of our superglue-based material: It isn’t made from oil and is easy to recycle.
When our material is heated to 410 degrees Fahrenheit (210 C), the long molecule chains made of repeating superglue units break apart into their small, individual superglue molecules. At this point, the superglue molecules turn into a vapor that is easy to separate out from a mixed waste stream of other plastics, paper, food residue, aluminum and other refuse commonly found in recycling waste streams. Once you collect the superglue vapor, you can cool it and turn it right back into our new plastic with over 90% efficiency.

What’s next?
Since superglue is inexpensive and already produced on an industrial scale, we imagine our method of creating superglue plastics should be easy to scale up. Finally, the machinery used to make superglue could also be used to recycle the superglue plastics and could be simply adapted into existing industrial processes.
Finding a replacement for polystyrene is a big step toward sustainable plastics, but polystyrene is only one of thousands of plastics used today. Our team is now designing superglue-based plastics with properties that resemble other kinds of commodity plastics, while still being easy to produce and recycle.
Scott Phillips receives funding from the Army Research Office.
Allison Christy does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Read These Next
Public defender shortage is leading to hundreds of criminal cases being dismissed
There are never enough lawyers to provide indigent defense, but the situation has gotten worse since…
Welcome to the ‘gray zone’ − home to nefarious international acts that fall short of outright confli
Nations are becoming adept at provocations that fall in the area between routine peacetime actions and…
The inspiring and tragic story of Mabel Stark, America’s most famous female tiger trainer
Long before Joe Exotic became Tiger King, Mabel Stark reigned as Tiger Queen.






