Supermoon! Red blood lunar eclipse! It's all happening at once, but what does that mean?
In the early morning of May 26, 2021, there will be a super blood-red lunar eclipse. The show will be spectacular and can all be explained by the orbits of the Earth and Moon.

The first lunar eclipse of 2021 is going to happen during the early hours of May 26. But this is going to be an especially super lunar event, as it will be a supermoon, a lunar eclipse and a red blood moon all at once. So what does this all mean?

What’s a super moon?
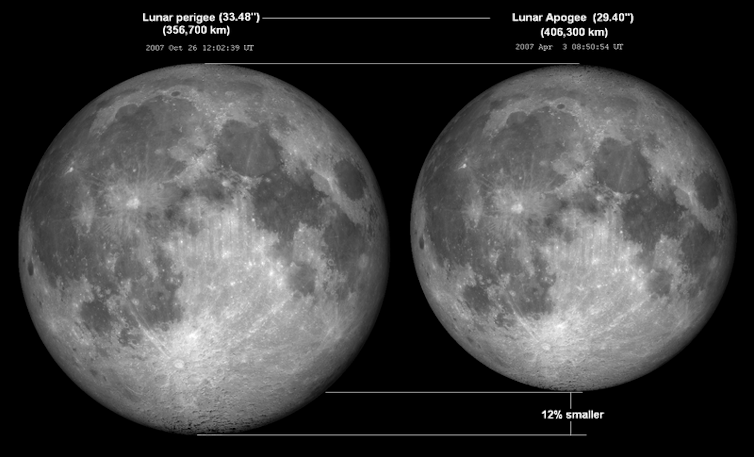
A supermoon occurs when a full or new moon coincides with the Moon’s closest approach to the Earth.
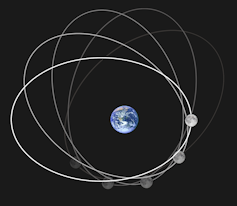
The Moon’s orbit around Earth is not perfectly circular. This means the Moon’s distance from Earth varies as it goes around the planet. The closest point in the orbit, called the perigee, is roughly 28,000 miles closer to Earth than the farthest point of the orbit. A full moon that happens near the perigee is called a supermoon.
So why is it super? The relatively close proximity of the Moon makes it seem a little bit bigger and brighter than usual, though the difference between a supermoon and a normal moon is usually hard to notice unless you’re looking at two pictures side by side.
How does a lunar eclipse work?
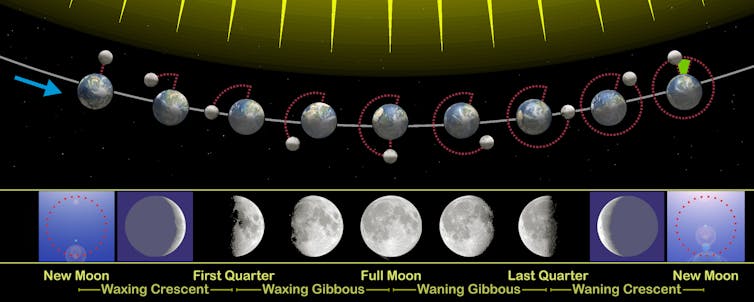
A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth’s shadow covers all or part of the Moon. This can only happen during a full moon, so first, it helps to understand what makes a full moon.
Like the Earth, half of the Moon is illuminated by the sun at any one time. A full moon happens when the Moon and the Sun are on opposite sides of the Earth. This allows you see the entire lit-up side, which looks like a round disc in the night sky.
If the Moon had a totally flat orbit, every full moon would be a lunar eclipse. But the Moon’s orbit is tilted by about 5 degrees relative to Earth’s orbit. So, most of the time a full moon ends up a little above or below the shadow cast by the Earth.
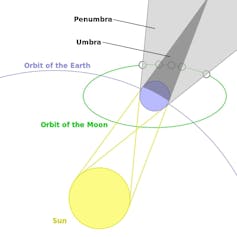
But twice in each lunar orbit, the Moon is on the same horizontal plane as both the Earth and Sun. If this corresponds to a full moon, the Sun, the Earth and the Moon will form a straight line and the Moon will pass through the Earth’s shadow. This results in a total lunar eclipse.
To see a lunar eclipse, you need to be on the night side of the Earth while the Moon passes through the shadow. The best place to see the eclipse on May 26, 2021, will be the middle of the Pacific Ocean, Australia, the East Coast of Asia and the West Coast of the Americas. It will be visible on the eastern half of the U.S., but only the very earliest stages before the Moon sets.
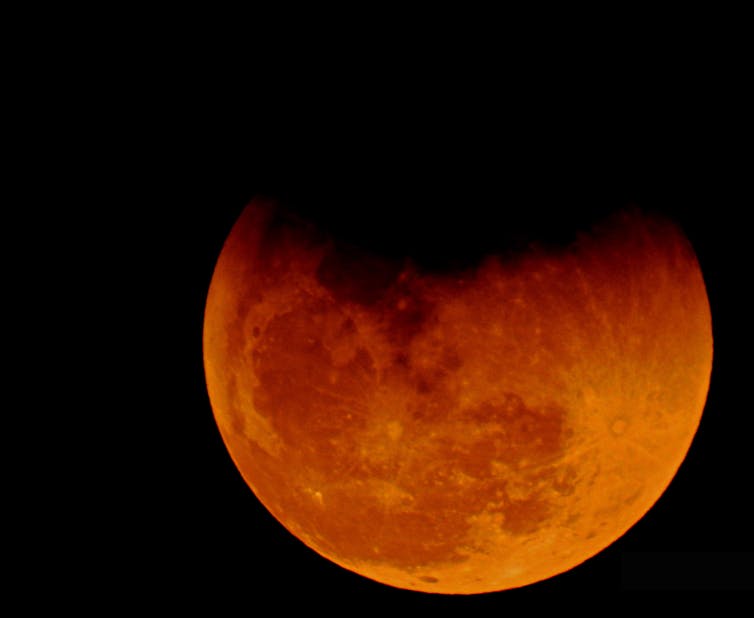

Why does the moon look red?
When the Moon is completely covered by Earth’s shadow it will darken, but doesn’t go completely black. Instead, it takes on a red color, which is why total lunar eclipses are sometimes called red or blood moons.
[Like what you’ve read? Want more? Sign up for The Conversation’s daily newsletter.]
Sunlight contains all colors of visible light. The particles of gas that make up Earth’s atmosphere are more likely to scatter blue wavelengths of light while redder wavelengths pass through. This is called Rayleigh scattering, and it’s why the sky is blue and sunrises and sunsets are often red.
In the case of a lunar eclipse, red light can pass through the Earth’s atmosphere and is refracted – or bent – toward the Moon, while blue light is filtered out. This leaves the moon with a pale reddish hue during an eclipse.
Hopefully you will be able to go see this super lunar eclipse. When you do, now you will know exactly what makes for such a special sight.
Portions of this story originally appeared in a previous article published on Jan. 24, 2018.
Shannon Schmoll receives funding from the Institute of Museum and Library Services and the National Science Foundation.
Read These Next
Why does pain last longer for women? Immune cells may be the culprit
Your immune systems kicks into gear when you’re injured, both worsening and relieving pain.
Honoring Colorado’s Black History requires taking the time to tell stories that make us think twice
This year marks the 150th birthday of Colorado and is a chance to examine the state’s history.
Florida’s proposed cuts to AIDS drug program threaten patient care and public health
Scaling back Florida’s AIDS Drug Assistance Program could mean a resurgence of HIV/AIDS and increased…






