Calling Asians 'robotic' is a racist stereotype with a long, troubled history
When Asian lives are reduced to negative stereotypes, those caricatures shape social interactions, deny Asian humanity and create the myth of the model minority.

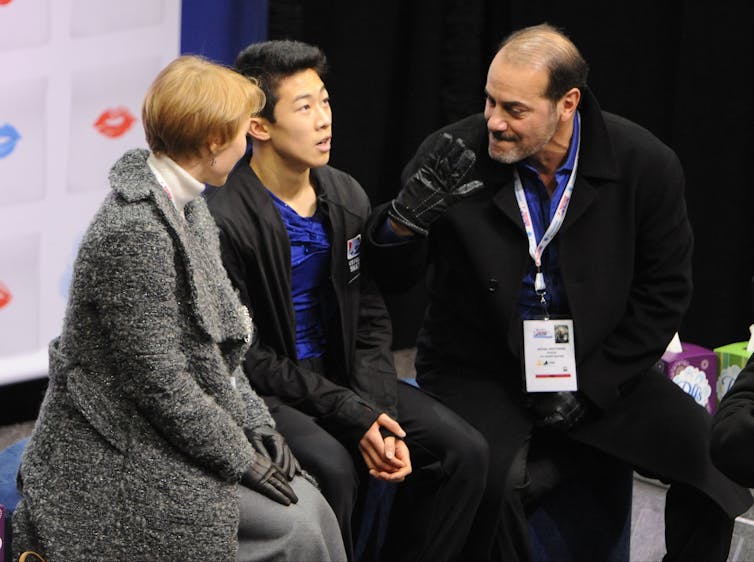
When U.S. figure skater Nathan Chen won the gold medal in men’s figure skating at the 2022 Winter Olympics, a Washington Post article attributed his win to a fierce, focused, “robotic” zeal. This robotic characterization draws on a dated stereotype of Asians as stoic, unfeeling workaholics.
In my book “Model Machines: A History of the Asian as Automaton,” I argue that the image of Asians as robotic serves as the perfect example of how majority cultures characterize a certain kind of minority as model workers and threats.
In the United States there has been a popular belief that Asian people are ruthless competitors obsessed with technical achievement, whether as classical pianists, spelling bee champs or math whizzes. This was the basis for the model minority myth. However, projections of the model minority often fuse into Asian roboticism, the notion that Asians act or behave like technological beings.
What happens when someone is seen as the perfect kind of human automaton?
Insofar as Asian lives are reduced to caricature, and their humanity disavowed, what emerges is a negative stereotype of Asians as uncreative cogs raised by “tiger parents” who teach their children total obeisance to authority, education researchers in Australia write.

Mental perceptions then shape social interaction.
In a 2009 study, social psychologists discovered that white people read East Asian faces as machinelike, bearing less-than-human qualities. This imaginary association bears a history, as media scholar Lisa Nakamura points out. When you brand someone as robotic, “you’re saying that what they make is not unique or worthy of recognition. Which is the history of Asian labor in the U.S.”
Representing Asians as automatons
When everyday people are rendered as robots, any sort of human rights are denied, and all sorts of abuses can occur.
As the China-U.S. trade war heated up in 2019, right-wing conspiracist Alex Jones claimed that Asians were like fearless “robots coming to kill you.”
The implication is that Chinese, Koreans and Vietnamese are a swarm of cyborgs who think alike and will attack in unison. Jones also stated that Native Americans – bearing some ancient link to Asia – are easy to “mind-control.”
Indeed, these disparaging references recall a long history of dehumanizing Asians and other groups.
As global capitalism developed alongside European colonialism, the thought that robots are mankind’s servants aligned with the treatment of colonial populations. In their 2019 book “Surrogate Humanity: Race, Robots, and the Politics of Technological Futures,” Neda Atanasoski and Kalindi Vora write that this “sliding scale of humanity” turned living subjects into objects of control.
The U.S. picked up on this in its quest for empire.
In the 19th century, Chinese workers were considered by Anglo-American politicians to be the world’s best laboring machines. This justified both their exploitation by and exclusion from the United States.
During World War II, U.S. military propaganda portrayed the Japanese soldier as a programmed warrior of the state, more animal than human. Amid the Cold War, the fiction of inexhaustible workers linked up with the fear of the masses in Asian communist nations.
Meanwhile, Vietnamese prostitutes were derided as “sex machines” by U.S. soldiers.

Today, Chinese factory workers are referred to as robots by their corporate managers, while promoters of South Korean popular music, or K-pop, categorize their singing idols as entertainment machines. Workers push against these insults, asserting their desires and freedom.
Challenging a stereotype
Scholars have adopted the term techno-orientalism to critique the view of the future as Asian dominated, especially in science fiction where Asians are figured as slaves to the machine.

Such harmful opinions are reproduced in mainstream movies like “Ex Machina,” which paints Asians as inscrutable bots. The Sundance hit “After Yang” depicts an android named Yang that reproduces this narrative.
Margaret Rhee, author of “Love, Robot,” says that the Asian as robot figure raises moral questions of solidarity, equality and justice. This resists the casting of Asians as material things.
The Smithsonian Asian Pacific American Center published a video essay, “Inhuman Figures,” that looks at this sense of Asians as tireless workers, robots, indistinguishable copies, clones and forever foreigners.
They supposedly lack human empathy and are, therefore, not deserving of compassion.
Whether subhuman or superhuman, Michelle N. Huang explains, Asians are never human enough.
[More than 150,000 readers get one of The Conversation’s informative newsletters. Join the list today.]
Long T. Bui does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Read These Next
How the Emerald Isle shaped the Steel City – Pittsburgh’s rich Irish history
Long before Pittsburgh’s modern Irish celebrations existed, Irish immigrants helped shape the city…
When US fights in the Middle East, American Muslim students often face discrimination
The war on terror is among the Middle East conflicts that sparked a rise of anti-Muslim and anti-Arab…
While the US government is investigating unidentified anomalous phenomena, academic researchers stud
Surveys have found that researchers studying UAPs can face pushback from mentors and colleagues, even…