Why do teachers make us read old stories?
Stories like 'Romeo and Juliet,' 'Alice's Adventures in Wonderland' and 'Jane Eyre' are still relevant today.


Curious Kids is a series for children of all ages. If you have a question you’d like an expert to answer, send it to CuriousKidsUS@theconversation.com.
Why do teachers make us read old stories? Nathan, 12, Chicago, Illinois
There are probably as many reasons to read old stories as there are teachers.
Old stories are sometimes strange. They display beliefs, values and ways of life that the reader may not recognize.
As an English professor, I believe that there is value in reading stories from decades or even centuries ago.
Teachers have their students read old stories to connect with the past and to learn about the present. They also have their students read old stories because they build students’ brains, help them develop empathy and are true, strange, delightful or fun.
Connecting with the past and present

In Shakespeare’s “Romeo and Juliet,” for example, teenagers speak a language that’s almost completely unfamiliar to modern readers. They fight duels. They get married. So that might seem to be really different from today.
And yet, Romeo and Juliet fall in love and make their parents mad, very much like many teens today. Ultimately, they commit suicide, something that far too many teens do today. So Shakespeare’s play may be more relevant than it first seems.
Additionally, many modern stories are based on older stories. To name only one, Charlotte Brontë’s “Jane Eyre” has turned up in so many novels since its original publication in 1848 that there are entire articles and book chapters about its influence and importance.
For example, I found references to “Jane Eyre” lurking in “The Princess Diaries,” the “Twilight” series and a variety of other novels. So reading the old story can enrich the experience of the new.
Building brain and empathy
Reading specialist Maryanne Wolf writes about the “special vocabulary in books that doesn’t appear in spoken language” in “Proust and the Squid.” This vocabulary – often more complex in older books – is a big part of what helps build brains.
The sentence structure of older books can also make them difficult. Consider the opening of almost any fairy tale: “Once upon a time, in a very far-off country, there lived …”
None of us would actually speak like that, but older stories put the words in a different order, which makes the brain work harder. That kind of exercise builds brain capacity.
Stories also make us feel. Indeed, they teach us empathy. Readers get scared when they realize Harry Potter is in danger, excited when he learns to fly and happy, relieved or delighted when Harry and his friends defeat Voldemort.
Older stories, then, can provide a rich depth of feeling, by exposing readers to a broad range of experiences. Stories featuring characters from a diverse range of backgrounds or set in unfamiliar places can have a similar effect.
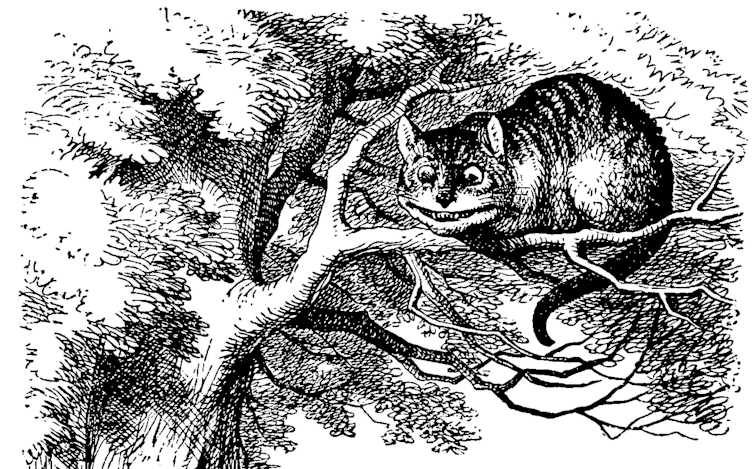

Reading can be fun
Old stories are sometimes just so weird that you can’t help but enjoy them. Or I can’t, anyway.
In Charles Dickens’ “Great Expectations,” there’s a character whose last name is “Pumblechook.” Can you say it without smiling?
In Lewis Carroll’s “Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland,” a cat disappears bit by bit, eventually leaving only its smile hanging in the air. Again, new stories are also lots of fun, but the fun in the older stories may turn up in those new stories.
For example, that cat returns in many newer tales that aren’t even related to Alice in Wonderland, so knowing the cat’s history can make reading that new story more pleasurable.
I won’t deny that some old stories contain offensive language or reflect attitudes that we may not want to embrace. But even those stories can teach readers to think critically.
Not every old story is good, but when your teacher asks you to read one, consider the possibility that you might build your brain, grow your feelings or have some fun. It’s worth a try, at least.
Hello, curious kids! Do you have a question you’d like an expert to answer? Ask an adult to send your question to CuriousKidsUS@theconversation.com. Please tell us your name, age and the city where you live.
And since curiosity has no age limit – adults, let us know what you’re wondering, too. We won’t be able to answer every question, but we will do our best.
[ You’re smart and curious about the world. So are The Conversation’s authors and editors. You can read us daily by subscribing to our newsletter. ]
Elisabeth Gruner does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Read These Next
The apocrypha, Christianity’s ‘hidden’ texts, may not be in the Bible – but they have shaped traditi
‘Apocrypha’ means ‘hidden’ in Greek, but it is often used to describe texts that are outside…
Minneapolis united when federal immigration operations surged – reflecting a long tradition of mutua
Minnesotans from all walks of life, including suburban moms, veterans and protest novices, have bucked …
How to prevent elections from being stolen − lessons from around the world for the US
As President Trump and other Republicans cast doubt on the legitimacy of the US electoral system, other…